How Project Management is Elevating Healthcare Facility Design
The ultimate goal of healthcare architecture and design is to create facilities that embody the highest standards of care. Healthcare construction projects are complex, requiring meticulous planning, coordination, and execution to meet stringent compliance regulations – in areas like layout, functionality, aesthetics, and the overall experience for patients, visitors, and staff.
With so many moving parts, the secret of pulling off a project seamlessly is having your systems and processes in place. Playbooks and templates are your best allies- they allow you to structure your creativity so that you are always mindful of timelines and budgets.
Kshititi Nagarkar, Shree Designs.
Effective project management is essential in healthcare construction, ensuring projects meet and surpass the expectations of providers and patients. It navigates the complexities of these projects, guaranteeing timely delivery, budget adherence, and high-quality standards.
This guide highlights the best practices and strategies healthcare architects and construction professionals employ to successfully execute healthcare projects, from new hospital constructions to clinic renovations.
Critical Components of Project Management in Healthcare Facility Design and Construction
Effective project management is the backbone of successful healthcare architecture, design, and construction projects. It encompasses various critical components, each contributing to the project’s overall success.
01. Project Planning and Initiation:
Good project management starts with setting clear objectives ensuring everyone knows the project’s goals. Detailed plans are then created, laying the roadmap to achieve these objectives. Skilled teams are assembled, with roles and responsibilities clearly defined to avoid overlaps and gaps.
02. Contract and Regulatory Compliance:
Managing contracts meticulously ensures that all parties fulfil their obligations and that the project adheres to agreed-upon terms. This includes reviewing contracts for potential risks, negotiating terms to protect the project’s interests, and ensuring timely payments to contractors and suppliers.
For instance, encountering an unexpected environmental regulation during construction could require quick renegotiation of contracts to include the necessary environmental safeguards. Ensuring compliance with all rules is another critical aspect. This means staying updated on building codes, healthcare regulations, and safety standards and incorporating these into the project planning and execution phases to avoid legal and financial penalties.
03. Budget Management:
Developing and closely monitoring project budgets are crucial. This involves preparing detailed cost estimates and financial forecasts, allowing for stringent expenditure control. An unexpected rise in material costs could threaten to derail a project’s budget. Project management can navigate such challenges through proactive financial forecasting and contingency planning, ensuring the project remains financially viable.
04. Resource Allocation:
Efficient allocation and optimisation of labour, materials, and equipment are essential for keeping a project on track. For instance, a delay in delivering critical building materials could stall the project. Effective project management counters this by securing materials well in advance and having backup suppliers, ensuring that work progresses as planned without unnecessary downtime.
05. Quality Control:
Setting and adhering to quality standards is non-negotiable. This involves regular monitoring and implementing quality assurance procedures to ensure that every aspect of the project meets the highest standards.
Consider a scenario where the work done by a subcontractor does not meet the project’s quality standards. Through regular quality inspections, project management can identify and rectify the issue early, maintaining the project’s overall quality.
06. Risk Management:
Identifying potential risks and developing strategies to mitigate them is a key component. Implementing these plans minimises disruptions. For example, a critical piece of medical equipment might be delayed. A risk management plan would include scheduling flexibility or finding temporary solutions, ensuring the project timeline is affected as little as possible.
07. Project Scheduling:
Developing and maintaining an accurate project schedule is vital. Adjustments may be needed to accommodate changes, ensuring the project’s timely completion. For instance, if an essential team member falls ill, good project management practices, such as cross-training team members, can keep the project moving forward by quickly reallocating tasks to cover the gap.
Continuous monitoring and evaluating project progress against set milestones allow for timely adjustments. This adaptability is crucial to maintaining project momentum and meeting completion dates.
08. Team Leadership and Communication:
Leading and motivating project teams effectively underpins successful project management. This involves setting clear goals, providing direction, and fostering an environment where team members feel valued and encouraged to contribute their best.
Maintaining clear and open lines of communication with all stakeholders, including clients, contractors, and team members, is crucial. Regular updates, meetings, and feedback sessions help identify potential issues early and align everyone with the project’s objectives.
09. Problem-Solving and Client Relations:
Addressing challenges promptly and maintaining strong client relationships are key to the success of any project. Effective project managers anticipate potential issues and have strategies ready to address them.
For example, a client may request a last-minute design change. In that case, the project manager must assess the impact, communicate the implications to the client, and find a solution that meets the client’s needs without derailing the project.
10. Health and Safety:
The well-being of all project participants is paramount. Enforcing strict safety protocols, conducting regular safety training, and ensuring all safety equipment is available and used correctly are essential practices. For instance, in an accident on site, having a well-practised emergency response plan can prevent severe injuries and save lives. Continuous monitoring and improving safety practices help create a safe working environment for everyone involved.
11. Project Closure and Evaluation:
Finalising project activities involves ensuring that all aspects of the project are completed satisfactorily, all contractual obligations have been met, and the client is satisfied with the outcome. Conducting a thorough evaluation after project completion helps identify lessons learned that can be applied to future projects.
For example, a post-project review might reveal that more efficient communication channels could have prevented inevitable delays, leading to new project management tools for future projects.
Each component plays a vital role in completing healthcare construction projects!
Adopting a Holistic Approach in Healthcare Construction
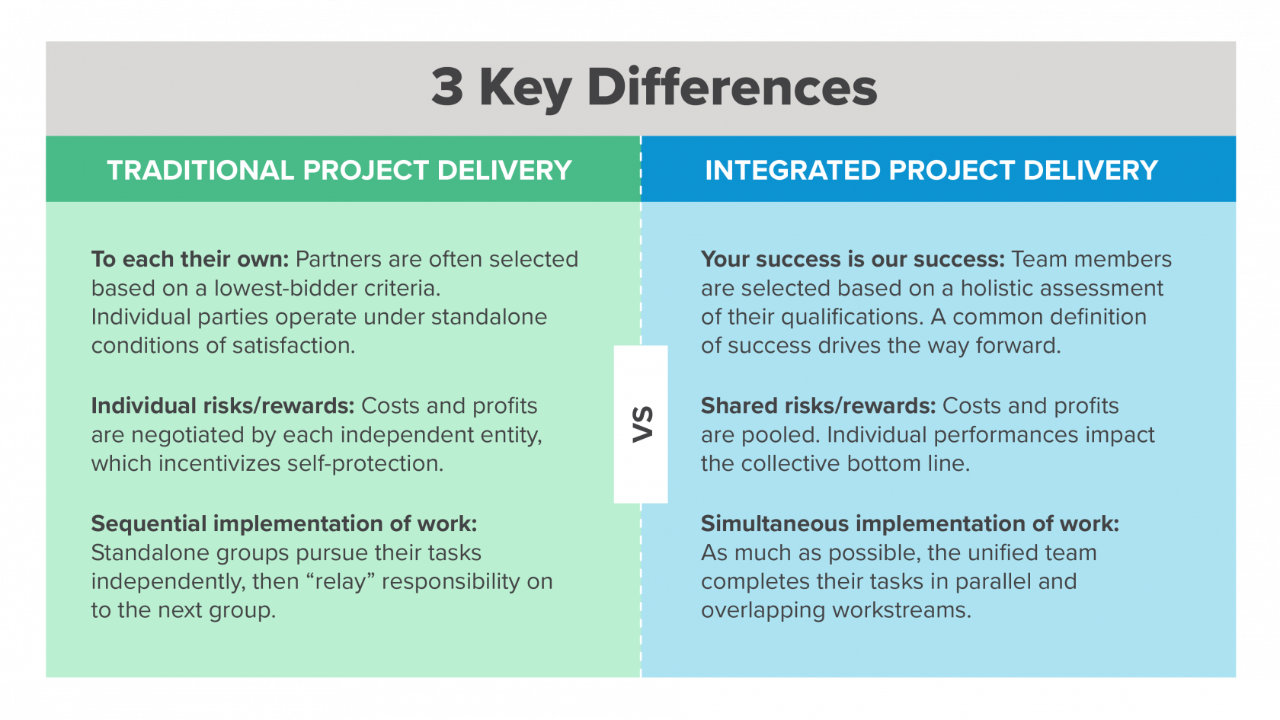
- Integrated Project Delivery (IPD): IPD brings together all stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and clients, in a collaborative environment to ensure seamless project execution.
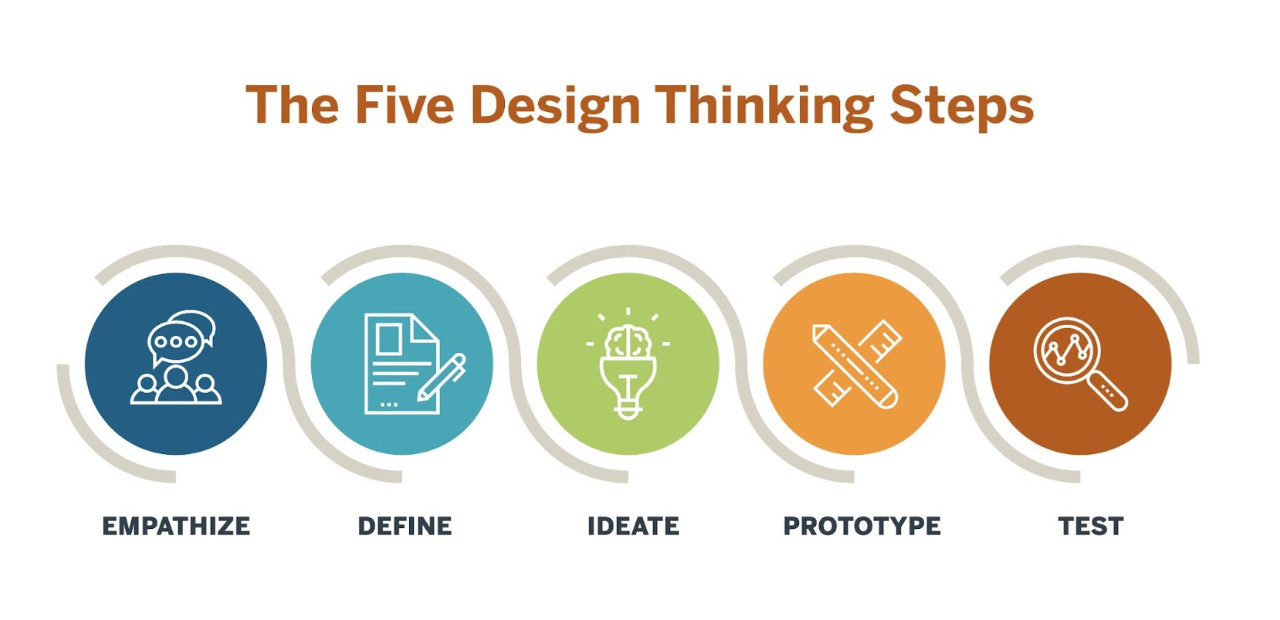
- Design Thinking encourages creative solutions to complex problems, enhancing the functionality and aesthetics of healthcare facilities.
- Agile methodology allows for flexibility in project management, accommodating changes in real-time and ensuring that the project progresses efficiently despite unforeseen challenges.
Utilizing Advanced Project Management Tools:
- Building Information Modeling (BIM) is pivotal in modern healthcare construction, offering a 3D visual representation of the project that enhances planning, design, and execution. It facilitates informed decision-making and improves project outcomes by allowing stakeholders to visualise the end product in detail before construction begins, identify potential issues early, and make necessary adjustments.
- Sophisticated project management software ensures projects stay on track. These tools offer real-time project overviews, making monitoring progress, managing budgets, and efficiently allocating resources easier. Making quick adjustments to schedules and resources in response to project developments is invaluable in maintaining project momentum and meeting deadlines.
Conclusion
” At Shree Designs, we use skilled project management to enhance project outcomes while meeting healthcare standards, significantly reducing delays and cost overruns. It’s the cornerstone of ensuring that every facility design project not only meets but exceeds the intended goals,” concludes Kshiti Nagarkar, Shree Designs.
Through strategic planning, risk management, and effective communication, project managers can navigate the complexities of healthcare construction, ensuring projects are delivered on time and within budget.
Related Posts
Designing Healthcare Facilities,Infographic,Project Management
Designing Healthcare Spaces That Truly Heal
From concept to completion, every medical space we design prioritizes patient flow, staff…
Designing for Disaster Preparedness
Hospital safety isn’t just about compliance—it’s about ensuring that your facility is safe,…
Building a Hospital from the Ground Up
Building a hospital is about much more than just bricks and mortar—it’s about creating a space that…
Tips for Picking the Right Healthcare Architecture Firm
Healthcare facility design is more than aesthetics - it directly impacts patient recovery, staff…
Building a Budget-Friendly Hospital: Optimizing Design & Costs
Planning a new healthcare facility on a budget? We understand the importance of maximizing value…
Value Engineering in Healthcare Architecture & Design
Navigating design and budget challenges can be tough, when building a healthcare facility. Value…
Navigating Risks in Healthcare Facility Development
We understand the complexities involved in planning a new healthcare facility. Unforeseen…
Budgeting Tips for Healthcare Architecture and Design
Navigating the financial aspects of designing and building a healthcare facility can be daunting.…
Tracking Metrics to Evaluate Design Efficacy
Unlock the Power of Design in Healthcare. Dive into our latest blog to explore essential metrics…









